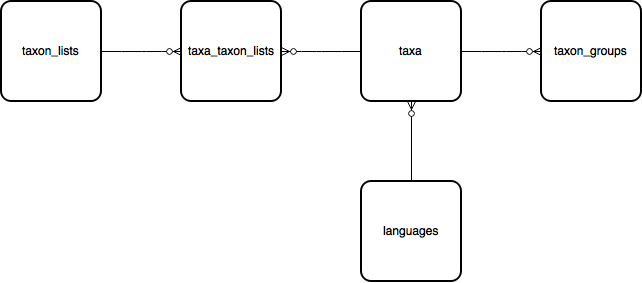
taxon_lists > taxa_taxon_lists > taxa¶
The second key part of the database is the taxonomy module which captures information about the species and other taxa which you can record against.
taxon_lists¶
The database stores multiple lists of taxa. A list can be anything from a simple flat list of a few species being recorded by a citizen science project to a full hierarchical taxonomy for a country’s species list.
Ref. taxon_lists
taxa_taxon_lists¶
The taxa_taxon_lists table serves to join taxa to the lists they belong to.
Ref. taxa_taxon_lists
taxa¶
The taxa table contains one row per taxon name. A single species concept, therefore, may have several rows in the taxa table, with one for the currently accepted name, plus others for synonyms and common names.
Here’s an example which grabs the taxon names in a list with common names:
select t.taxon, string_agg(distinct tc.taxon, ', ') as common
from taxa_taxon_lists ttl
join taxa t on t.id=ttl.taxon_id
left join (taxa_taxon_lists ttlc
join taxa tc on tc.id=ttlc.taxon_id and tc.deleted=false
join languages lc on lc.id=tc.language_id and lc.iso<>'lat'
) on ttlc.taxon_meaning_id=ttl.taxon_meaning_id
where ttl.deleted=false
and ttl.taxon_list_id=1
and ttl.preferred=true
group by t.taxon
Don’t worry if that query is looking a bit complex, later we’ll see how the reporting cache tables make querying both observational and taxonomic data much simpler.
In the taxonomy module, there are several different “key” fields which can be used to refer to database records in different ways:
taxa_taxon_lists.id (taxa_taxon_list_id) is the primary key of every instance of a unique taxon name within a taxonomic checklist or hierarchy. Every accepted latin name, synonym and common name has a unique identifier. Generally when linking an occurrence to its identification we use the taxa_taxon_list_id because it gives a precise reference to the exact name used and the list it was selected from - reports can easily work out from this the currently accepted name or common name for output for example.
preferred_taxa_taxon_list_id is the taxa_taxon_list_id of the currently accepted name on the list. It can be used to quickly identify a group of all the given names for a taxon on a list since they will all share the same preferred_taxa_taxon_list_id.
The taxa_taxon_lists.taxon_meaning_id field contains an ID that is unique for each species concept so can be used to easily locate and translate between the different names available for a taxon. This is very similar to the preferred_taxa_taxon_list_id except that taxon_meaning_id can be shared across lists (when the list creator chooses to do so). This means that if you select all the records which have the same taxon meaning ID you will get all the given combinations of taxon names and species checklists across all lists.
The taxa.external_key field is often used to store an externally recognised identifier for the taxon. In the UK it is used to store the preferred Taxon Version Key as used in the UK Species Inventory (UKSI). TVKs are also used by the NBN to identify taxa.
Ref. taxa
taxon_groups¶
The taxon_groups table provides a list of labels (sometimes called reporting categories) which are often used in reporting to help clarify taxon names in a user friendly way. Each taxon belongs to a single taxon group and group names can be taxonomic but don’t have to be, for example a taxon group could be called “aquatic insects” if desired.
Ref. taxon_groups
languages¶
A simple lookup list of languages used in the taxonomy and termlists parts of the database, e.g. separates Latin names from English names. Includes the 3 letter iso language code which can be used as a shortcut to the full language name.
Ref. languages
